Integrated Business Planning, or IBP for short, is a strategic management process that connects various organizational departments to align business operations with financial goals. How? By integrating business functions – such as Sales, Marketing, Finance, Supply Chain and Operations – to create a holistic view of the company’s performance and future direction. This blog post offers a comprehensive guide to discuss what precisely IBP entails and how Finance can drive business results and collaboration within the organization via a robust and comprehensive IBP process.
What Is Integrated Business Planning?
While the business world and Finance have always had shared language and acronyms, some new (and reimagined) acronyms may now be flooding your feed. One such topic you may be hearing a lot about lately is Integrated Business Planning (IBP). Yet the concept of IBP isn’t new. In fact, it’s related to Sales & Operations Planning (S&OP), a concept that’s been around awhile.
Still, IBP may seem overwhelming in the context of all the different acronyms related to financial and operational planning floating around lately. For example, IBP, S&OP, eXtended Planning and Analysis (xP&A) and others are just a few acronyms muddying the waters. But this comprehensive guide to all things IBP aims to help demystify the process.
So what, exactly, is IBP?
IBP ultimately aims to unify business strategy with planning, budgeting and forecasting activity for all business lines and functions – providing one version of the numbers. In turn, a trusted, common view of the numbers provides a robust baseline for agile decision-making. That common view also keeps all teams collectively trying to achieve the same corporate objectives while staying focused on specific KPIs. In other words, the different teams maintain their independence while working in unison to achieve corporate success by leveraging the same trusted and governed data.
The bottom line? IBP is about aligning strategy intent, unifying planning processes and bringing the organization together.
How Integrated Business Planning Works
The IBP process is a framework to address the C-suite needs and help implement the business strategy and manage uncertainty to improve decision-making. So what’s the secret sauce of IBP to make all of that happen? A collaboration between the different teams under a single view of the numbers that must unequivocally be tied to financial performance. That’s how the C-suite gets value from IBP. Consequently, Finance plays a central role in the IBP process.
IBP typically focuses on horizons of 24-60 months, as opposed to the short term. That focus equates to Integrated Tactical Planning or Sales and Operations Planning and Execution. Since the process must be fully integrated, it removes the departmental silos. Plus, the IBP process must adapt to the organizational construct of every business (IBP isn’t a one-size-fits-all type of process).
A typical IBP process involves several stages:
- Data Collection and Analysis: Gathering relevant data (e.g., sales forecasts, production capacities, inventory levels and financial projections) from different departments.
- Demand Planning: Predicting future demand based on historical data, market trends, customer feedback and sales forecasts.
- Supply Planning: Determining the resources and capabilities (e.g., materials, production capacity and distribution channels) needed to meet the forecasted demand.
- Financial Planning: Developing financial plans and budgets aligned with the demand and supply forecasts, considering factors such as revenue targets, cost structures and investment requirements.
- Scenario Planning: Creating alternative scenarios to assess how different strategies, market conditions or external factors impact business outcomes.
- Management Business Review: Collaborating across departments to make informed decisions on resource allocation, investments, pricing strategies and operational adjustments.
- Execution and Monitoring: Implementing the plans, tracking performance against targets, and continuously monitoring key metrics to identify deviations and take corrective actions.
The most efficient way to foster this collaboration is through a unified solution and data model that caters to the needs of the various agents involved on each review. In fact, Figure 1 shows how one solution gathering all the capabilities in the greyed area under a unified data model is the most efficient approach to IBP.
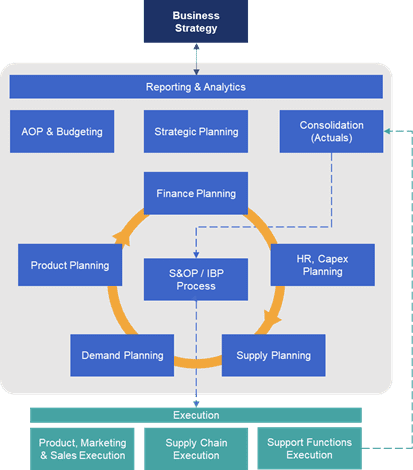
Figure 1: A Unified Data Model for IBP
Core Elements and Stages of the Integrated Business Planning Process
The IBP process includes the following core elements:
- Governance Structure: Establishing a cross-functional team with representatives from key departments to oversee the IBP process, define roles and responsibilities, and ensure alignment with organizational goals.
- Data Integration: Integrating data from different systems and sources to create a single source of truth for decision-making, using technologies such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, Corporate Performance Management (CPM) tools, business intelligence (BI) tools and data analytics platforms.
- Collaborative Planning: Encouraging collaboration and communication between departments to share insights, align objectives and develop consensus-based plans that support overall business objectives.
- Continuous Improvement: Implementing feedback loops, performance reviews and process refinements to enhance the effectiveness and agility of the IBP process over time.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Integrated Business Planning
Some key KPIs to measure the effectiveness of an IBP process include:
- Forecast Accuracy: Comparing actual sales or demand with forecasted figures to assess the accuracy and reliability of forecasting models.
- Inventory Turnover: Calculating how often inventory is sold and replaced within a specific period indicates efficiency in inventory management.
- Customer Service Levels: Monitoring metrics like on-time delivery, order fulfillment rates, and customer satisfaction scores to measure service performance.
- Financial Metrics: Evaluating financial KPIs such as revenue growth, gross margin, operating profit, and return on investment (ROI) to gauge overall business performance.
- Supply Chain Performance: Assessing metrics like lead times, supplier performance, inventory levels, and supply chain costs to optimize supply chain operations.
Technological Enablers for Integrated Business Planning
Several technological enablers support a robust IBP process:
- ERP Systems: Integrated ERP systems consolidate data from different departments, automate processes, and provide real-time visibility into business operations.
- BI and Analytics Tools: Business intelligence tools and analytics platforms enable data visualization, trend analysis, scenario modeling, and predictive analytics for informed decision-making.
- Collaboration Platforms: Cloud-based collaboration tools facilitate communication, document sharing, and workflow management among cross-functional teams involved in IBP.
- Advanced Planning Software: Specialized IBP software solutions offer capabilities for demand planning, supply chain optimization, financial modeling, scenario planning, and performance monitoring.
- AI and Machine Learning: AI-driven algorithms and machine learning techniques can enhance forecasting accuracy, identify patterns, optimize resource allocation, and automate repetitive tasks in IBP processes.
By leveraging these technological enablers, finance professionals can streamline the IBP process, improve decision-making, and drive business growth.
In conclusion, Integrated Business Planning (IBP) is a strategic approach that aligns business functions, integrates data-driven insights and fosters collaboration to achieve operational excellence, financial stability, and competitive advantage. By implementing a robust IBP process supported by technology and focused on continuous improvement, finance professionals can effectively drive sustainable growth, mitigate risks, and adapt to evolving market dynamics.
Learn More
Want to learn how you can maximize the benefits of your IBP process and get leadership on board with the plan? Check out our eBook Unifying Integrated Business Planning Across Finance and Supply Chain. You’ll learn how to unify IBP across Finance and Supply Chain teams and read about use cases as proof points. Plus, you’ll gain an understanding of the unique capabilities OneStream’s Intelligent Finance Platform brings to unify Finance and Supply Chain planning activities.
Learn MoreGet Started With a Personal Demo



